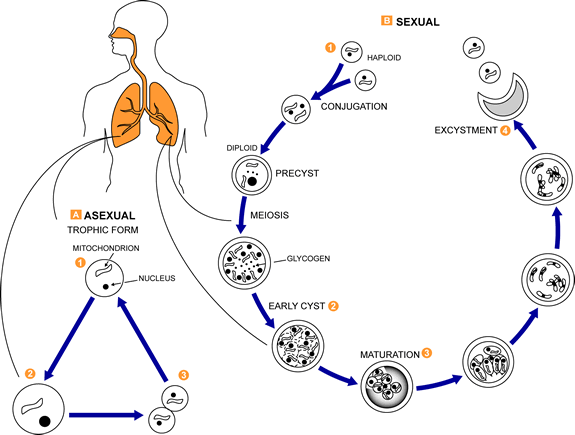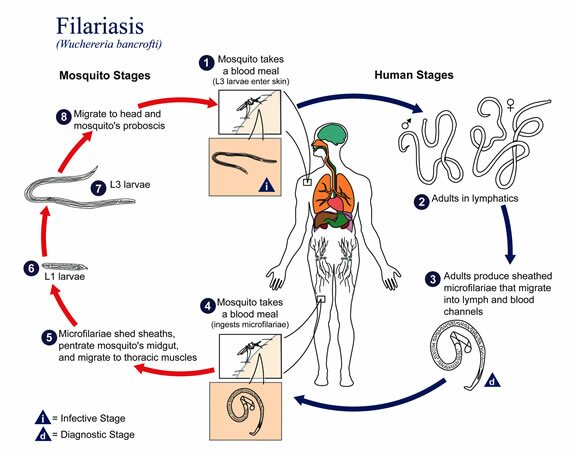

 Wuchereria Bancrofti. The term ‘filariasis” covers a dozen or so species of nematodes. Adult forms of the kind parasitize in the absorbent glands or in the connecting tissue. They are characterized by a filiform long body (from several to more than dozen centimetres). Females deliver alive filiform larvas, which are several hundred µm long. This larvas often occur in the blood or the skin and under the conjunctiva. Bloodsucking insects like: mosquitoes, gad-flies and blackflies transmit these nematodes. Humans become infected with the invasive larvas by being bitten. The nematodes occurring in humans are: Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Onchocerca volvulus, Loa loa.
Wuchereria Bancrofti. The term ‘filariasis” covers a dozen or so species of nematodes. Adult forms of the kind parasitize in the absorbent glands or in the connecting tissue. They are characterized by a filiform long body (from several to more than dozen centimetres). Females deliver alive filiform larvas, which are several hundred µm long. This larvas often occur in the blood or the skin and under the conjunctiva. Bloodsucking insects like: mosquitoes, gad-flies and blackflies transmit these nematodes. Humans become infected with the invasive larvas by being bitten. The nematodes occurring in humans are: Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi, Onchocerca volvulus, Loa loa.
Wuchereria Bancrofti occurs in the wide geographic lane between the tropics. Several species of mosquitoes like: Aedes, culex, Anopheles transmit Wuchereria Bancrofti . Adult worms settle in the absorbent glands and vessels. Microfilariae appear in the blood during the night, only in the Oceania islands it does not have any clear day cycle. Around the mature worms in the absorbent glands, the vessels, the liver and the spleen a granulomatous tissue comes into being which causes, after a dozen or so years, irreversible adhesive and calcification lesions of the lymphatic system. They lead to vessel thickening (e.g. in the groin), bursting large absorbent vessels, hydrocele and elephantiasis of the limbs, reproductive organs or nipple.The invasion of Wuchereria Bancrofti is mostly asymptomatic, especially among people who were exposed to infection for a short time. In intense or repeatable infestations, the symptoms might appear after a year and might not characteristic:
More characteristic are further complications:
Burugia malayi
First of all it is different from Wuchereria bancrofti as it occurs in South Asia and Far East and it infects only 1 – 16 % of the total population. Moreover, it has a considerable reservior in monkeys, dogs and cats and is transmitted exculsively by gnats from the Mansonia family. Symptomatic infestations occur among children as a complex consisting of eosinophilia, enlargement of the peripheral and celiac absorbent glands and pneumonitis. This filariasis causes elephantiasis of the feet and shin. It occurs on Flores and Timor islands (Indonesia). Brugia timori infestations have a very rough clinical course.
Onchocerca volvulus
It occurs in Central Africa and some of the countries of Central and South America. The parasite is transmitted by small insects, so called black-flies, developing in rivers with a strong current. Mature worms develop in the subcutaneous tissues, especially in the torso, the head and the legs creating tumors with a diameter of several centimeters. O. volvolus microfilariae appear in the whole skin of the body and in the eyeballs which results in conjunctiva, choroid, retina inflammation and cornea damage. The most serious complication after onchocercosis is blindness caused by corneal opacity, secondary glaucoma and eye lesions.
Loa loa
It occurs only in Central – West Africa and is transmitted by bitterns from the Chrysopos group. Adult forms penetrate subcutenous tissue or conjunctiva causing skin swelling or blushing and echema lesions. Calabar swelling, that is periodical painful lesions around dead parasites, usually around big joints, where parasites are under the biggest threat of external injuries. Glottis oedema and cephalitis are the most dangerous complications of loaosis. Microfilariae might appear occasionally in the blood but only during the day.


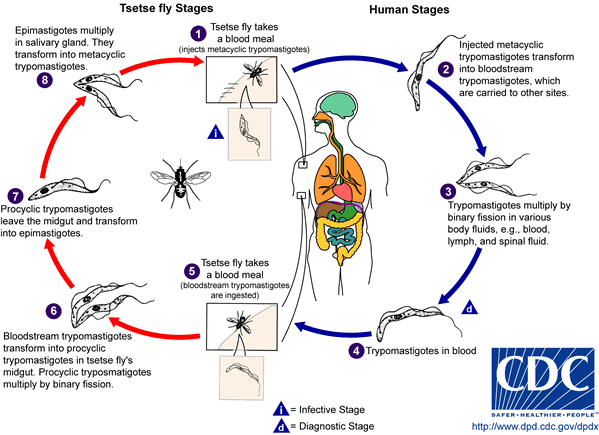
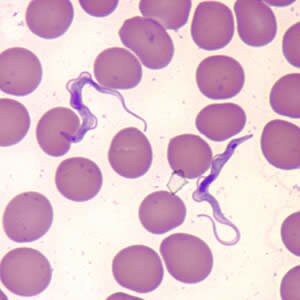 Trypanosoma gambiense. It is a group of animal cholimastix represented by bowel parasites of invertebrates, blood parasite of vertabrates and rubber-plant milk parasites. Their body is long and they reproduce by longitudinal division.They move by using its waving membrane. They are transmitted by biting insects and leeches. The shape of their bodies change when the host is changed. Some of them have pathogenic activity like: Trypanosoma gambiense transmitted by tse-tse fly and causing African sleeping sickness.
Trypanosoma gambiense. It is a group of animal cholimastix represented by bowel parasites of invertebrates, blood parasite of vertabrates and rubber-plant milk parasites. Their body is long and they reproduce by longitudinal division.They move by using its waving membrane. They are transmitted by biting insects and leeches. The shape of their bodies change when the host is changed. Some of them have pathogenic activity like: Trypanosoma gambiense transmitted by tse-tse fly and causing African sleeping sickness.
Infection symptoms:
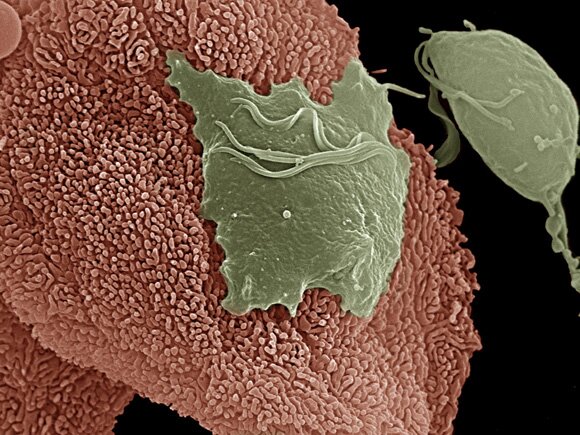
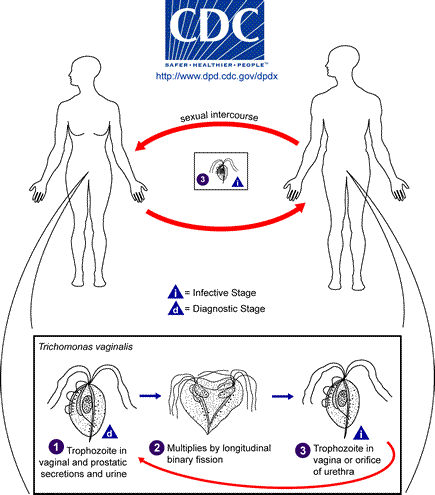
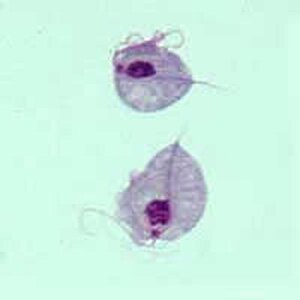 Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomonas vaginalis is quite common in Europe and it belongs to chilomastix family which is mainly sexually transmitted. In chronic inflammatory states, in case of women, it can be found in the vagina or urethra and when it comes to men it occurs in the urethra and prostate and seminal gland.
Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomonas vaginalis is quite common in Europe and it belongs to chilomastix family which is mainly sexually transmitted. In chronic inflammatory states, in case of women, it can be found in the vagina or urethra and when it comes to men it occurs in the urethra and prostate and seminal gland.
Pregnant women can transmit the disease to their babies while giving birth (it usually disappears after a month). Trophozoites of the size of 7×10 cm cause vagina epithelium cells damages, small losses and ulceration. The hatching period lasts 1 – 4 weeks. 50% of infected women suffer from ample foaming yellow vagina discharge and it is accompanied by vagina and vulva irritation. The symptoms intensify during menstruation. Medical examination can proove an iflammation of the vagina, an increased amount of mucus in the vagina or its damage.Trichomoniasis is often complicated by bacterial and fungal infection. Trichomoniasis treatment intensifies candidosis activity as a result of changes in vaginal biocenosis. Chronic trichomoniasis might influence pelvis minor inflammatory states, infertility, pregnancy complications, the length of convalescence period after hysterectomy. In case of men the trichomonas might embed in the urethra, prostate gland, testicles and penis ulceration.The invasions generally show no symptoms and it must be distinguished from infection and diploccocus gonorrhoea.
Trichomoniasiasis complications
It is usually accompanied by bacterial and fungus infection (e.g. Candidia albicans). If it is chronic and not cured it can cause infertility and serious pregnancy complications.
Trichomonas vaginalis symptoms:
When an infection of the reproductive ducts is accompanied by a urethra ducts infection there is a possibility of itchiness, over-urination or painful urination and pain in the lower part of the stomach.
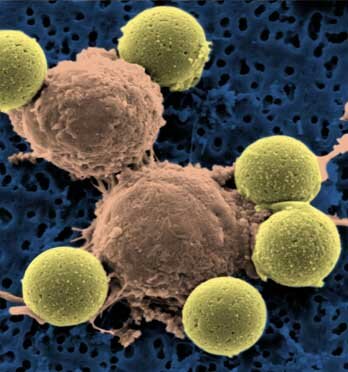
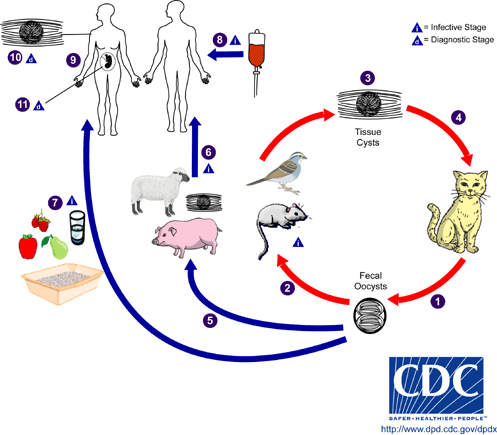
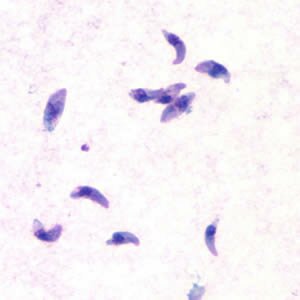 Taxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii). Infectious disease of men and animals which is a result of protozoon – endocell organisms - infestation into different human organs. Toxoplasmosis is caused by toxoplasma gondii and belongs to cholimastix class of the protozoon kind. Cats are typical hosts. In their intestinal epithelial cells the whole life cycle takes place consisting of sexual and asexual phases. Two forms of the disease can be distinguished: acquired and inborn. Acquired toxoplasmosis does not have one clear clinical shape. It takes place when an infected female cat passes germs onto its foetus. It might cause miscarriage or pathological changes in characteristic locations that become visible in the offspring during the first years of life.
Taxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii). Infectious disease of men and animals which is a result of protozoon – endocell organisms - infestation into different human organs. Toxoplasmosis is caused by toxoplasma gondii and belongs to cholimastix class of the protozoon kind. Cats are typical hosts. In their intestinal epithelial cells the whole life cycle takes place consisting of sexual and asexual phases. Two forms of the disease can be distinguished: acquired and inborn. Acquired toxoplasmosis does not have one clear clinical shape. It takes place when an infected female cat passes germs onto its foetus. It might cause miscarriage or pathological changes in characteristic locations that become visible in the offspring during the first years of life.
Acquired toxoplasmosis symptoms:
Chronic toxoplasmosis symptoms:
Inborn toxoplasmosis symptoms:
Infection sources:
Disease course
The parasite moves from the alimentary canal of a human into the absorbent glands, the muscles, the brain, the spinal cord and the eye balls. The course of the disease can be quite asymptomatic. However often the following symptoms may occur: enlarged absorbent glands, constipation, rarely – heart muscle inflammation or meningitis. The infection of women before they get pregnant does not carry any risk for the future foetus (however there are still some specialist who do not agree with this thesis). Fresh infection of a pregnant woman causes an inflammation of the placenta and this way the parasites may penetrate into the foetus. The risk of toxoplasmosis penetration through the placenta increases along with the pregnancy progress: 25% – in the first trimester, 50% – in the second one and 65% – in third one. Whereas in the inborn form of toxoplasmosis the risk is the highest in the first trimester and equals 75%, in the second one – 50% and the third one – 5%.
Inborn toxoplasmosis might cause foetal hypertrophy, thrombocytopenia, enlarged liver and spleen. Natural miscarriage or intrauterine death occur in the first trimester of the pregnancy. Symptomatic inborn toxoplasmosis occurs in 30% of infected infants, 10% of which suffer from its acute course.
Perinatal death rate caused by inborn toxoplasmosis is estimated at 8%. 70% of prenatally infected children do not show any symptoms and in most of them the disease is left undetected and not cured. In some children at later age certain consequences connected with the central nervous system, hearing handicap and vision disorders might appear.
Who is the most vulnerable to toxoplasmosis infection ?
Toxoplasmosis infection risk increases with age. Research has shown that mothers who gave birth to a child with Down syndrome had the positive result of an analysis on toxoplasmosis in 80% of cases; women with pathologica obstetric anamnesis – 60%; the mentally ill – 40 – 50% and people with eye sickness – 50 – 60 %.
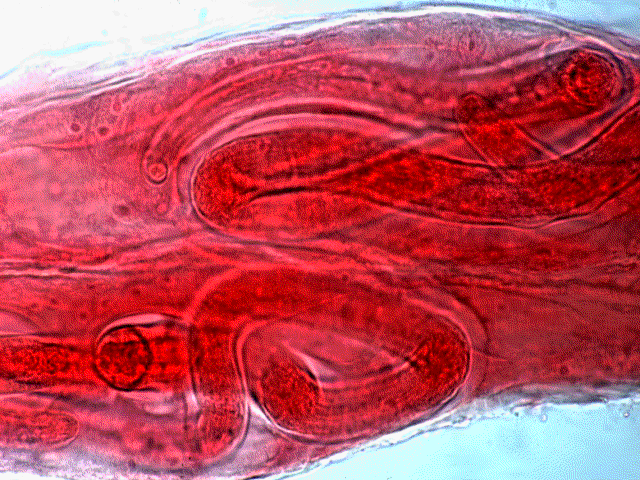
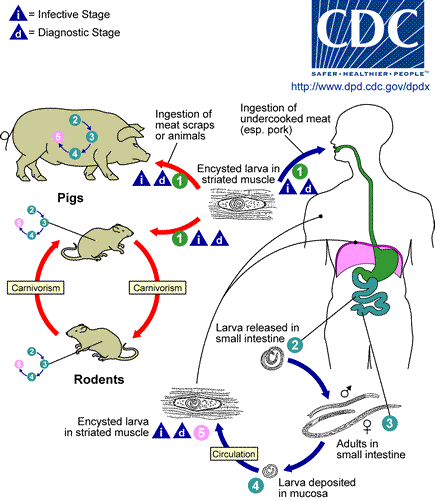
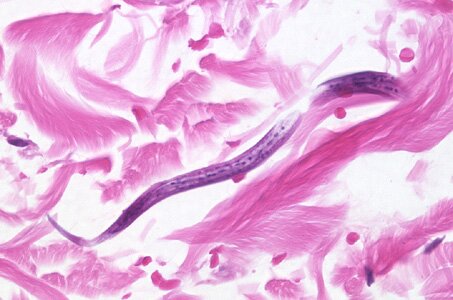
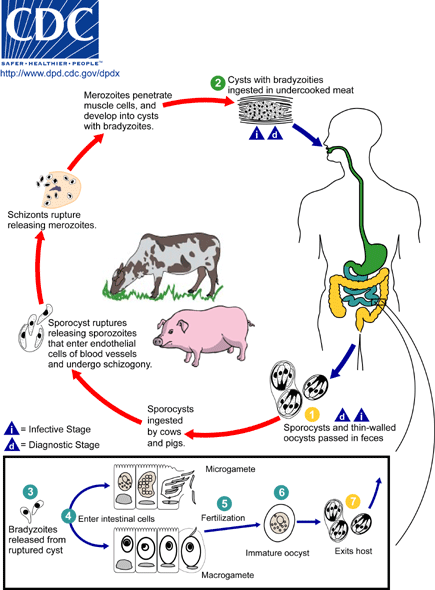
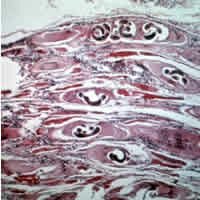 Threadworm (trichinella spiralis). A small nematode – females grow 3mm long and males about 1,5mm. Mature forms of the threadworm develop in the small bowel within several days from swallowing invasive larvas. On the sixth day from the infection, the females start to produce larvas which move into the tissue through the blood and lymph. The larvas develop in the muscle tissues and within 6 weeks they encyst. A certain amount of larvas survive in the human organism for dozen or so years.
Threadworm (trichinella spiralis). A small nematode – females grow 3mm long and males about 1,5mm. Mature forms of the threadworm develop in the small bowel within several days from swallowing invasive larvas. On the sixth day from the infection, the females start to produce larvas which move into the tissue through the blood and lymph. The larvas develop in the muscle tissues and within 6 weeks they encyst. A certain amount of larvas survive in the human organism for dozen or so years.
Trichinosis, caused by threadworms, occurs on all continents where people eat animal meat which may contain the threaworms. The animals which can cause the infection are: pigs, wild boars, bears, dogs, cats and rats. However it is the most dangerous to eat dishes made of raw or undone meat.
Sanitary negligence and lack of hygiene (feeding pigs with carcass, presence of rats) are the most common causes of trichinosis. The majority of infections among men are caused by eating raw meat containing nomatodes. Most of them show no symptoms. Even if the symptoms are visible it still does not mean the disease is serious or light.
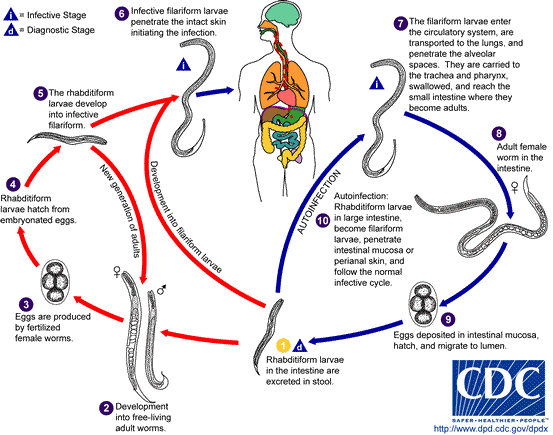
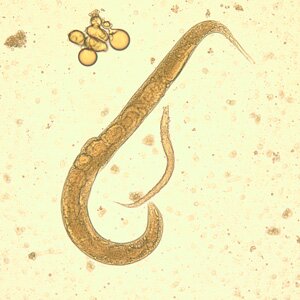 Strongyloides stercoralis. Strongyloides stercoralis is one of few parasites that can live independently in soil, rich in minerals. It occurs in tropical and semi-tropical countries. People can be infected by touching filiform invasive larvas. The infection causes a disease concerning the alimentary canal.
Strongyloides stercoralis. Strongyloides stercoralis is one of few parasites that can live independently in soil, rich in minerals. It occurs in tropical and semi-tropical countries. People can be infected by touching filiform invasive larvas. The infection causes a disease concerning the alimentary canal.
A female form of Strongyloides stercoralis is a tiny 2mm-long nematode. It lives in the duodenum and leiunum mucosa membrane, rarely in the lung tissue. They lay eggs in tissues, from which rabdoidal larvas are hatched. Then they exit the body with faeces or they are coughed out. Sometimes rabdoidal larvas, still in the bowel or in the anus area, can develop into invasive filarial forms which might infect others. The infection might last for decades.
Infection sources
Larvas get into the body through the skin on the feet or buttocks, leaving blush skin changes itching and withering lasting a couple of hours or days. Short-term line lesions on the abdomen and anus come into being as a result of auto-invasion of a person who is already infected. During strongyloides stercoralis’ way through the lungs tissue, Loeffler’s infiltrations might appear. Less intense invasions result in small lesions in the mucosa membrane and the small bowel.
Strongyloides stercoralis symptoms:
Massive invasions cause lesions in the duodenum and leiunum.
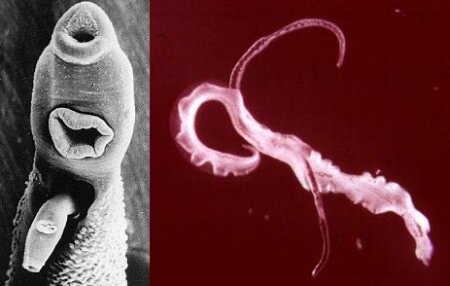
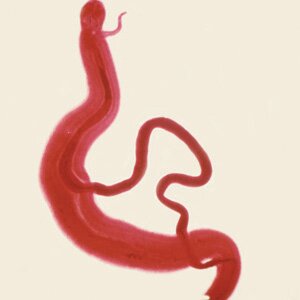 Schistosomiasis (Schistosoma japonicum). It is the most significant parasitological problem after malaria worldwide. Nowadays, there are over 200 million people infected with the disease all over the world.
Schistosomiasis (Schistosoma japonicum). It is the most significant parasitological problem after malaria worldwide. Nowadays, there are over 200 million people infected with the disease all over the world.
Infection symptoms:
Development cycle
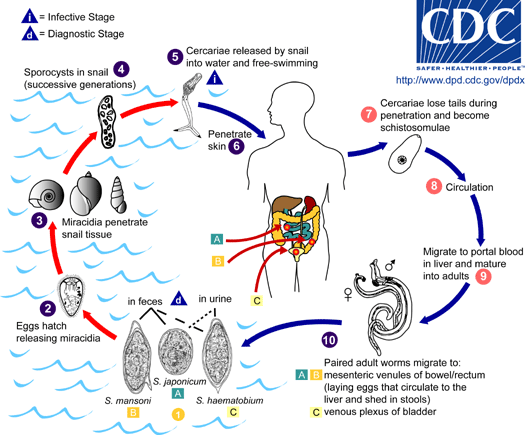
The life cycle of Schistosomiasis is tightly connected with water environment, which is contaminated by human faeces and urine. Wild animals and pets are hosts for only S.japonicum. Schistosoma evolve in water and land snails. Cercarias released to water by snails infect humans by penetrating the skin and getting into the blood vessels. In order to prevent infection you should not bathe in contaminated water reservoirs or drink watar of unknown origin.
Mature forms of S. haematobium evolve in the blood vessels of the pelvis minor especially in the bladder whereas S. mansoni i S. japonicum in the mesenteric veins. Part of eggs laid by the female living several years penetrate the tissues into the bladder or large bowel and are passed through with faeces or urine. Another part of eggs stay in the tissues causing chronic pathological lesions.
The local consequences of S. heamatbium infestation are: blood and inflammatory lesions, later hypertrophic and papillary lesions of bladder walls and the pelvis minor organs. As a result of the lesions, extensive calcifications and cicatrization of the bladder. That leads to bacterial infection of the urinary tract, clots, uremia and anaemia. The main symptoms in the urinary system schistosomiasis are painful urination and hematuria (especially in the final part of the urine)
S. mansoni i S. japonicum infestations cause bleeding lesions and ulceration then polypoid and scars of the small and large bowel mucosa.
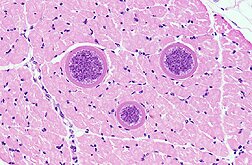
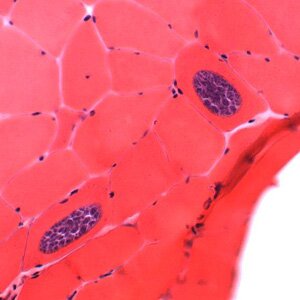 Sarcocystis hominis. Sarcocystis hominis is a rarely occuring protozoon from Sarcocystidae family (coccidian subtype), affecting men by sarcoscytisis – a disease affecting the small bowel and the muscle tissue. Infections occur all over the world.
Sarcocystis hominis. Sarcocystis hominis is a rarely occuring protozoon from Sarcocystidae family (coccidian subtype), affecting men by sarcoscytisis – a disease affecting the small bowel and the muscle tissue. Infections occur all over the world.
The infection frequency has not been confirmed and it is estimated at more than 10%, and it affects mostly children.
How do people get infected?
An infection starts in the oral cavity and gets there with water and food that are poisoned by sporocyst.
Sarcocystis hominis infection symptoms:
Sarcocystis hominis affects people causing muscle or alimentary system sarcocyst.
The acute stadium is characterized by:
The chronic stadium of sarcocyst, when flukes might be embeded in the muscle tissue of different parts of the body is chraceterized by:
Sarcocystis hominis development cycle
There are 3 stadiums of agamogony (taking place in muscles) and other stadiums of agamogony taking place in the bowel. Sarcocystis hominis development cycles are: sporocyst, sporozoite, schizont, merozoite, micro and macrogametes, zygote, oocyst and others. When a sporocyst enters a human organism it gets transformed into a sporozoit, which then is converted into a schizont in the bowel epithelium cells. Schizonts divide several times and become merozoites, which convert into macrogametes or together with blood macrophages get into the muscle tissue (e.g. bowel), creating sarcocysts fulfiled with bradyzoites,. Microgametocytes, during the reproduction process produce micrgamets and macrogametocytes produce macrogamets. Gametes colligate creating a zygote surrounded by a capsule and as a result an oocyst is created. Subsequently, the cyst is excreted with faeces, and becomes a subject of further division creating invasive sporocyst.
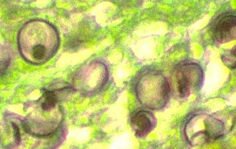 Pneumocystis jiroveci (carinii). Pneumocystis jiroveci – previously known as Pneumocystis carinii (classified as a protozoon at that time) is a fungus causing pneumacystosis. It affects people with a weaker immunity like: children and the elderly but these are rather occasional cases. Most cases of Pneumocystis jiroveci infections constitute as AIDS infection symptoms. The fungus occurs in the digestive system of most pets and domestic animals (dog, cats, cattle and horses) however they very rarely infect healthy organisms. Generally, this germ infects persons suffering from AIDS, large bowel cancer or people having thier immune systems handicapped in some sort of way. Pneumacytosis is detected by colouring the sputum with silver.
Pneumocystis jiroveci (carinii). Pneumocystis jiroveci – previously known as Pneumocystis carinii (classified as a protozoon at that time) is a fungus causing pneumacystosis. It affects people with a weaker immunity like: children and the elderly but these are rather occasional cases. Most cases of Pneumocystis jiroveci infections constitute as AIDS infection symptoms. The fungus occurs in the digestive system of most pets and domestic animals (dog, cats, cattle and horses) however they very rarely infect healthy organisms. Generally, this germ infects persons suffering from AIDS, large bowel cancer or people having thier immune systems handicapped in some sort of way. Pneumacytosis is detected by colouring the sputum with silver.