Common roundworm (ascaris lumbricoides)

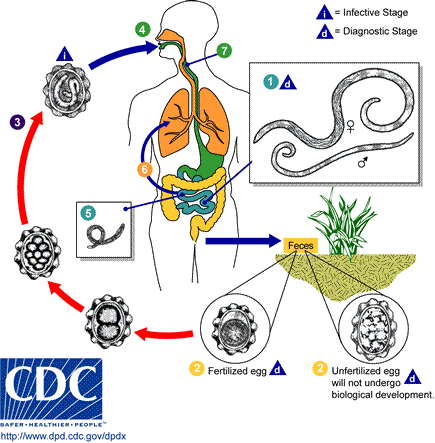
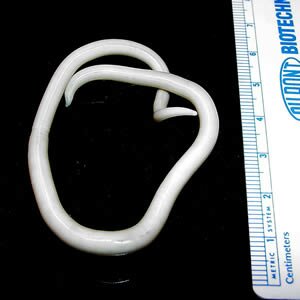 Common roundworm (ascaris lumbricoides). Ascaris is a large nematode living in the small bowel. Females grow 20-35 cm long and 3-6mm wide whereas males can be 15-30cm long and 2-4 mm wide. Ascaris lives from 6 to 18 months, during that time it produces 65 million eggs which are later excreted with faeces. Ascaris causes a disease called ascariasis, which is the most frequent helminthiasis of the alimentary canal – about 1 billion infections.Intensive invasions and complications are the reason of a considerable amount of deaths worldwide – 20 000 a year. It occurs mostly in tropical countires. A man is the only final host of ascaris. Eggs excreted with faeces get into the outside environment (soil, sewage), where it grows up and takes an invasive form. The man swallows an egg and , as a result of digestive juices activity, a larva emerges and starts penetrating the organism. It gets through the walls of the small bowel to the vessels of secondary veins then it moves through the liver, the heart to the lungs. From the lung cells it gets to the bronchia then to the windpipe and with the mucus to the alimentary system where it reaches its maturity. Such penetrating larvas might cause bowel and liver wall damages, lesions in the lungs and eosinophilosis. A mature ascaris causes digestive and nervous system disorders. There is a possibility of : stomachache , loss of appetite, dizziness, vomiting, constipations, diarrhoea, bowel occlusion, bile duct obturation. Sometimes allergic skin lesions, face swelling, conjunctivitis and cough might occur. Children suffer from sleep disorders, hyper-excitability, loss of attention. In order to recognise the infection a stool examination should be carried out.
Common roundworm (ascaris lumbricoides). Ascaris is a large nematode living in the small bowel. Females grow 20-35 cm long and 3-6mm wide whereas males can be 15-30cm long and 2-4 mm wide. Ascaris lives from 6 to 18 months, during that time it produces 65 million eggs which are later excreted with faeces. Ascaris causes a disease called ascariasis, which is the most frequent helminthiasis of the alimentary canal – about 1 billion infections.Intensive invasions and complications are the reason of a considerable amount of deaths worldwide – 20 000 a year. It occurs mostly in tropical countires. A man is the only final host of ascaris. Eggs excreted with faeces get into the outside environment (soil, sewage), where it grows up and takes an invasive form. The man swallows an egg and , as a result of digestive juices activity, a larva emerges and starts penetrating the organism. It gets through the walls of the small bowel to the vessels of secondary veins then it moves through the liver, the heart to the lungs. From the lung cells it gets to the bronchia then to the windpipe and with the mucus to the alimentary system where it reaches its maturity. Such penetrating larvas might cause bowel and liver wall damages, lesions in the lungs and eosinophilosis. A mature ascaris causes digestive and nervous system disorders. There is a possibility of : stomachache , loss of appetite, dizziness, vomiting, constipations, diarrhoea, bowel occlusion, bile duct obturation. Sometimes allergic skin lesions, face swelling, conjunctivitis and cough might occur. Children suffer from sleep disorders, hyper-excitability, loss of attention. In order to recognise the infection a stool examination should be carried out.
Disease syptoms
- cough
- bronchia spastic states
- fever
- eosinophiliosis and leukocytosis
- small bowel mucosa nematode lesions
- undetermined chronic stomachaches
- dizziness
- occasional vomiting
- loss of appetite
- apathy and movement over-excitation
- sleep disorders
- conjunctivitis, eyelids inflammation
- skin lesions
- rhinitis
- bowel contraction states
- allergic symptoms
- convulsions
- faintings
- dyspnea
Infection sources
- digestive system infections may start by swallowing eggs, delivered into your mouth by dirty hands, contaminated food or water
- the outside environment (soil, water)
- eating raw vegetables and fruit from gardens fertilized with human faeces
- children playing in a playground
- adults working in the field or garden
A man can not be infected directly by another man
Disease course
Larvas which get into the alimentary system penetrate through the bowel wall into the circulatory system. They flow with the blood and embed in the lungs, then they move through the bronchi to the windpipe where they are coughed out and swallowed again. After getting to the small bowel again, the larvas transform into mature individuals (female-25-35 cm long and male 15-25cm) and live there for a year or two. tion.
Who is the most prone to have ascaris
Children between 3 and 10 are the most likely to be infected with ascaris.