Dwarf tapeworm (Hymenolepis diminuta)
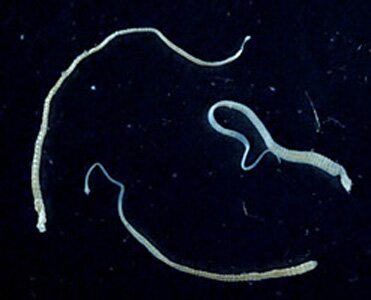
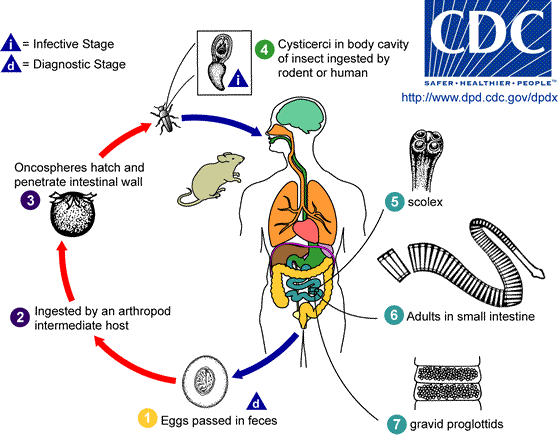
 Dwarf tapeworm (Hymenolepis diminuta). It is relatively small, 2 – 5 cm long. Its head is equipped with hooks and suckers. The parasite is common among rats and mice and men as well, occuring mostly in closed environments, especially among children. It induces a disease known as hymenolepiasis. Its development cycle can be conducted in one host. In the bowel, eggs released from the ending segments are partially excreted and some penetrate into the mucosa, where they get mature. The cysticercoids are released that begin tapeworm strobila. The development lasts about 3-4 weeks. The eggs can be transported from man to man by hands, food, water and insects or by self-contamination. The dwarf tapeworm can lead to bowel villuses damages by cystticerkoids development. The activity of toxins excreted by this tapeworm has not been examined yet. Clinical observations show that infection intensity in a man is regulated by immune mechanisms. When it comes to adults, the infection intensity is rather small, clinical symptoms are hardly recognizable. In case of children, the amount of parasite eggs, excreted with faeces, are partially absorbed, often depending on a child’s health state. Small and malnourished children suffer from very intensive invasions.
Dwarf tapeworm (Hymenolepis diminuta). It is relatively small, 2 – 5 cm long. Its head is equipped with hooks and suckers. The parasite is common among rats and mice and men as well, occuring mostly in closed environments, especially among children. It induces a disease known as hymenolepiasis. Its development cycle can be conducted in one host. In the bowel, eggs released from the ending segments are partially excreted and some penetrate into the mucosa, where they get mature. The cysticercoids are released that begin tapeworm strobila. The development lasts about 3-4 weeks. The eggs can be transported from man to man by hands, food, water and insects or by self-contamination. The dwarf tapeworm can lead to bowel villuses damages by cystticerkoids development. The activity of toxins excreted by this tapeworm has not been examined yet. Clinical observations show that infection intensity in a man is regulated by immune mechanisms. When it comes to adults, the infection intensity is rather small, clinical symptoms are hardly recognizable. In case of children, the amount of parasite eggs, excreted with faeces, are partially absorbed, often depending on a child’s health state. Small and malnourished children suffer from very intensive invasions.
Children infection symptoms
- loss of appetite
- loss of weight
- vomiting
- stomachache
- restlessness
- convulsions
- sleep disorders