Human louse (Pediculus humanus)
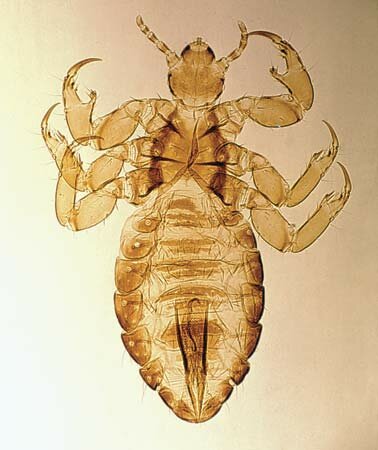 Human louse (Pediculus humanus). Men are the main hosts of the species. It is divided into two subspecies: a body louse (Pediculus humanus corporis) and a head louse (Pediculus humanus capitis). The body louse’s eggs stick to human clothes mostly to underwear seams and clothes of natural textile. They seldom stick to hairy part of the chest or the armpit. The head flea embeds on the head, neck or back hair.
Human louse (Pediculus humanus). Men are the main hosts of the species. It is divided into two subspecies: a body louse (Pediculus humanus corporis) and a head louse (Pediculus humanus capitis). The body louse’s eggs stick to human clothes mostly to underwear seams and clothes of natural textile. They seldom stick to hairy part of the chest or the armpit. The head flea embeds on the head, neck or back hair.
Lice are white-gray. Female individuals grow 2 – 4,7 mm long and males are smaller. The front of its head is narrow and its abdomen is oval without side spicules. They find appropriate conditions to grow in a humidity environment and temperature 28-31ºC. Their lifetime depends on the humidity level, temperature and nutritional status. Lice live only on men. The smell of human sweat attracts lice. The sweat composition and especially the lactic acid it contains determine the choice of the host. The head lice live mainly in the hair near ears or on the back of the head whereas the body lice live on theese parts of the body that are covered with clothes. Lice spread by a direct contact or an indirect one that is by the use everyday items like: combs and brushes or sleeping in the same bed. Children attending primary school are most likely to have the head lice because of weak hygene. The body lice occur mostly in regions with cold or moderate climate where people wear worm clothes for the most time of the year.
The bite spot is characterized by itchy inflammatory clods. Scratching them might cause secondary bacterial infection. Pus flows out of the ijuries and leaves scabs. Lymph nodes around the spot grow bigger and hurt when they are touched. The duration of the disease depends on their location in the hair. Their eggs stick to the hair at the bottom and move away from the skin as the hair grows. White eggs in the hair prove pediculosis.
Body pediculosis occurs mostly among soldiers, the homeless or prisoners. When lice are sucking blood their salivary glands put saliva into the body which makes the skin red and itchy. Scratching causes secondary bacterial infection. Some small scars might occur. The disease that is caused body louse activity is called “vagabond disease”. The disease might be recognized by a different colour of the sking and itching feeling.
Prevention
- head examination among children
- keep your clothes and body clean
- keep public places like: hostels, hospitals, dormitories and hair dresser’s clean.





