Hydatid tapeworm (Echinococcus granulosus)
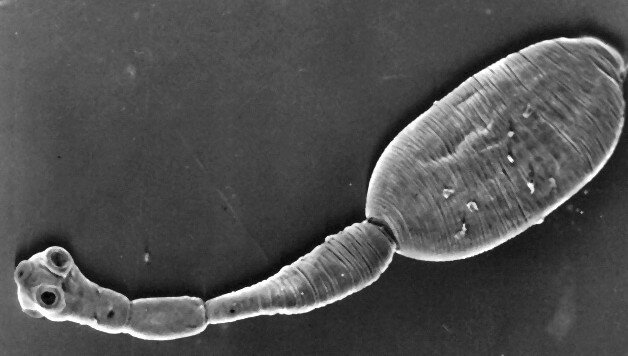
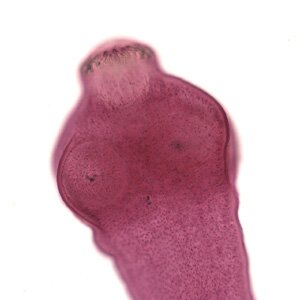 Hydatid tapeworm (Echinococcus granulosus). A clinical view of echinococcosis has the features of a cancer, which may lead to death in ten years.
Hydatid tapeworm (Echinococcus granulosus). A clinical view of echinococcosis has the features of a cancer, which may lead to death in ten years.
Echinococcosis symptoms – symptoms and consequences depend on larvas location, their size and the amount of blisters.
1. Liver echinococcosis symptoms:
- blood vessels and bile ducts pressure can appear after several or dozen or so years after infection
2. Pressure on the blood vessels:
- secondary hypertension
3. Pressure on the bile ducts leads to:
- jaundice
- bile duct inflammation
4. Lung echinococcosis in its initial state can be detected accidentally, during routine lungs x-rays. Big and numerous blisters, which lead to changes as a result of pressure on the lung tissue. The symptoms are:
- dysponoea
- cough
- blood cough
- shortening of breath
- chest pains
5. If larvas are in the spleen the organ is enlarged and secondary infections occur.
6. When they are in the kidneys, the symptoms are:
- organ enlargement
- urinate problems
- kidney area pains
- blood and proteins in the urine
7. Larvas located in the bones may cause to the bone tissue to collapse
8. The earliest and the most acute clinical symptoms are in case of blisters located in the brain or eye ball suggesting tumor.
Larvas in such important organs, can lead to the death of the host, which happens when the diagnosis of echinococcosis is not always on time and the necessary treatment is not conducted.
Pharmacological treatment not always brings the result we expect. Moreover, it can’t be always surgically removed (taking its size into concideration, no surgical access or proximity to other tissues and the danger of injury), an accidental blister burst during an operation can lead to secondary echinococcosis. The blister burst and secondary echinococcosis can occur independently, when the blister grows so big that the organs or tissues in which the larva has embeded do not allow its further growth or as a result of mechanical injury. The secondary echinococcosis is a spreading of protoscolexes in the host organism, which can lead to an anaphylactic stroke and that generally causes death.
How the infection happens
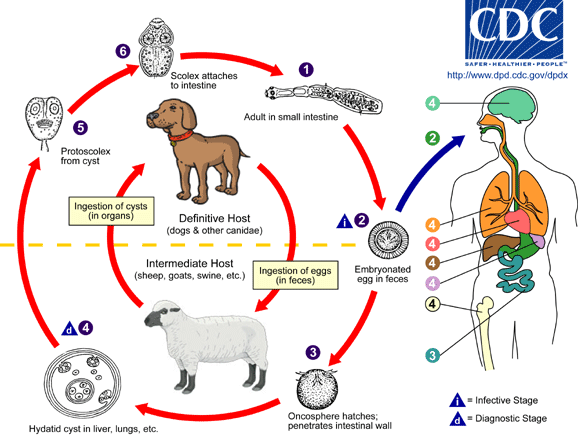
Echinococcosis is caused by hydatid tapeworm larvas (Echinococcus granulosus lub Echinococcus multilocularis). The main sources are: infected dogs, cats, foxes and wolves. The infected animals excrete larva eggs and contaminate the environment. People can become infected by hydatid tapeworm by direct contact with an infected pet, it refers especially to kids who while playing with the pets take the tapeworm eggs into their mouth. An indirect source of infection can be dirty fruit and vegetables and other types of food prepared or kept in non-sanitary conditions. Rodens and small mammals, raw meat and the bowels of other animals can be the source of infection for pets, by eating the food with agressive forms of parasite. They become infected and excrete eggs in their environment. The infection of humans not always results in a disease, it depends on an individual immune system, and not every larva of a tapeworm will find suitable conditions for development in a human body. Additionally, only a few animals are infected with a tapeworm, so the echinococcosis is rarely found among people.
However you should not underestimate the disease as it is extremely dangerous. When it occurs, without the necessary treatment, it can lead to very acute, chronic and often irreversible complications and even to death.
Epidemiologists appeal not to eat forest berries, wild strawberries or raspberries without washing as these plants are often a “hotel” for a hydatid tapeworm. It causes echinococcossi which destroys our organism like a cancer. Specialists from The Military Hygiene Institute tested several jars of forest blackberries, every second jar contained hydatid tapeworm eggs.
Hydatid tapeworm development cycle
Hydatid is a very aggressive parasite. Its larvas after getting into an organism embed in the most important parts of the human body: the liver (over 90% cases), lungs and brain. Around the larva, a cyst is created which grows bigger and presses on the neighbouring tissues. The final hosts of the hytadis are carnivorous animals, mostly wild ones in which the parasite closes its development cycle. Echinococcisis does not have to show any symptoms for 10-15 years. The parasite reproduces itself and spreads on other organs creating metastasis like cancer. The burst of a cyst can be dangerous for life.