Lamblia (Giardia duodenalis)
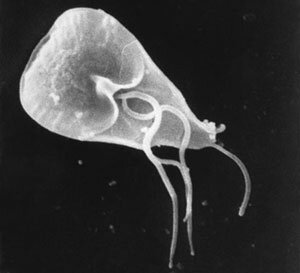 Lamblia (Giardia duodenalis).
Lamblia (Giardia duodenalis).
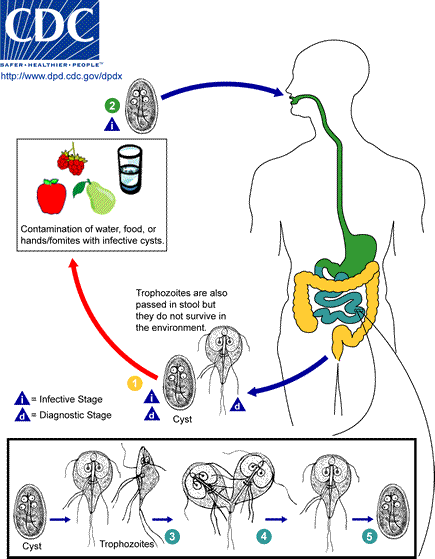
Lamblia (Giardia duodenalis) is a protozoom living mostly in the bowel (generally in the duodenum and the bile ducts).
Lamblia mostly inhabits the alimentary canal, the duodenum, the bile ducts, 1 cm of length contains 1000 lambia members. Lamblias sticks to the bowel. Its presence causes digestion problems, allergies, nutrient deficiency. Every tenth person infected with lamblia feels seek, the rest do not show any symptoms. The detection of lambia is a difficult task.
A single treatment is not sufficient, lamblia cysts can survive and another invasive forms can be created.
Lamblia occurs mostly in the alimentary canal.
Lamblia cysts spread through water systems or insects. Sometimes drinking water containing lamblia cysts can even start an epidemy.
Lamblia can produce toxins.
Lamblia existing in the bile ducts can threaten the liver or duodenum but it can also irritate the pancreas and infect it as a result.
Germs and parasites , which are inside of us, eat food that we consume and excrete as well, which is very toxic for our organism. It is very difficult to get rid of lamblia or staphylococcus so hygiene and your own body observation is essential.
Toxins excreted by this parasites cause:
- hemoglobin level decrease
- constipation
- unfresh breath
- oxidation disorders
- toxic poisoning of the organism
Lamblia induces gall bladder stones, duodenum and pancrease problems.
Lamblia worms prefer sugar, refined products as they strengthen them the most. If somebody likes sweets then he is more prone to invasive infections caused by this protozoon.
Lamblia presence examination:
- examining faeces is not effective enough therefore cell examinations are recommended
Immunoenzymatic tests are 89 – 95% accurate. They consist in examining faeces in search for specific enzymes produced by tropozoid.
Wild animals and pets are lamblia hosts.
Lambliasis is a parasite disease caused by a lamblia infection of the small bowel and liver. Human infections not always show clinical symptoms. Most people are healthy hosts.
Lambliosis symptoms:
- pain resembling ulcers, liver colic or gall stones attack
- diarrhoea or constipation
- opulent strongly stinking stools
- subfebrile body temperature
- allergic rush
- anaemia
- bowel infection
- liver infection
- stomach rumble
- heartburn
The bowel infection can cause a totally exhausting feeling. X-rays detect duodenal cup and gall bladder function disorders. Rarely, pain in the right part of the hip can occur. Lambliosis liver infection can be characterized by an inflammation of the gall bladder, the bile duct, the small bowel and colon or even cirrhosis of the liver. A gall bladder inflammation caused by lamblia is accompanied by strong pain like an acute colic in the liver or chronic pains increasing while eating. It can sometimes lead to vomiting, salivatin, diarrhoea, jaundice and high fever. A gall bladder inflammation caused by lamblia, without a secondary infection, can imitate bile stones. Sometimes a faster heart beat might suggest interference in the heart-vascular system. Symptoms such as nervous system disorders shown in tiredness, irritation, apathy, tearfulness, headache, temperature disturbances, kids’ slow growth, metabolism disorders, loss of weight, trembling fingers and increased sweating might be caused by toxins.
Infection sources
Parasites can get into our body with food and water or even during sexual anal intercourses. Persons with a weak immunity are more vulnerable to infections. They start a disease leading to absorption disorders of fat, carbohydrates, vitamin B12 and folic acid in the small intestine which leads to malnutrition and anaemia. In the bowels, lamblia creates oval cysts 10-14 cm long. Bad sanitary conditions stimulate lamblia extension.