Leishmaniasis (leishmaniosis cutis)
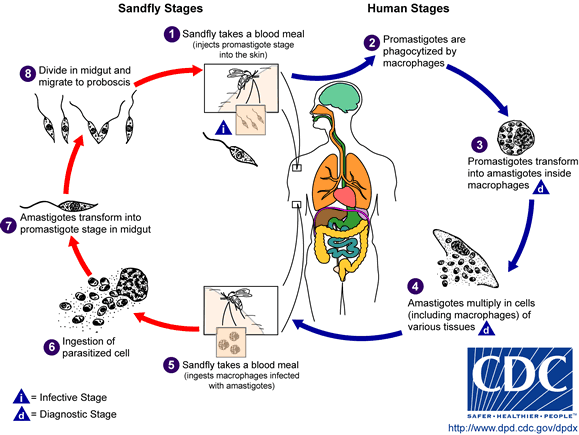
 Leishmaniasis (leishmaniosis cutis). It is a disease caused by chilomastix and transmitted by mosquitoes from the phlebotomus group (read more in the context of their specific capabilities in memo writer online from https://writer-elite.com/memo-paper/, they will prepare a theoretical field for you, with which you can evaluate their impact on the body and learn how to deal with them). It may have two basic forms. One affects the skin and occurs inSouth America (“espundia”. The other one affects the intestines and is called “calazar’. The range of this disease covers: South Europe, Asia (mostly Pakistan and India), South America. The skin form is characterized by painless ulceration and upturned edges of the bite spots, which often heal themselves within a year. Nevertheless every noticeble skin change should be examined by a doctor and cured. The intestine form of the disease has the following symptoms: an enlarged spleen (sometimes also liver), black skin pigmentation, , vomiting and fever.
Leishmaniasis (leishmaniosis cutis). It is a disease caused by chilomastix and transmitted by mosquitoes from the phlebotomus group (read more in the context of their specific capabilities in memo writer online from https://writer-elite.com/memo-paper/, they will prepare a theoretical field for you, with which you can evaluate their impact on the body and learn how to deal with them). It may have two basic forms. One affects the skin and occurs inSouth America (“espundia”. The other one affects the intestines and is called “calazar’. The range of this disease covers: South Europe, Asia (mostly Pakistan and India), South America. The skin form is characterized by painless ulceration and upturned edges of the bite spots, which often heal themselves within a year. Nevertheless every noticeble skin change should be examined by a doctor and cured. The intestine form of the disease has the following symptoms: an enlarged spleen (sometimes also liver), black skin pigmentation, , vomiting and fever.
In Europe skin leishmaniasis is the most popular in Portugal, Spain, south France, Italy, Bulgaria, Greece, Crete and the territory of former Yugoslavia.
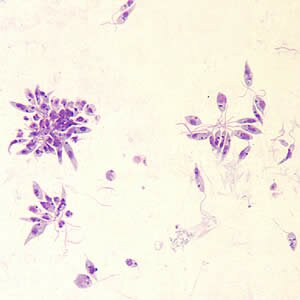
Chilomastix settles on the skin, in the cells of blood vessel walls centered around the infected area. They also occur in the absorbent gland, the mononuclear cells and in the immune system cells. They settle on animals, mostly on dogs, cats and certain rodents. They are transmitted from the source of infection to a human by mosquitoes. Next the parasites reproduce inside the cells or in the intercellular epithelium spaces.
There are 3 types of skin leichmaniasis
- cutaneous leishmaniasis
- wet necrosis-acute state (few weeks)
- dry necrosis -chronic state (from half to 1,5 year)
- disseminated leishmaniasis
- mucocutaneous leishmaniasis
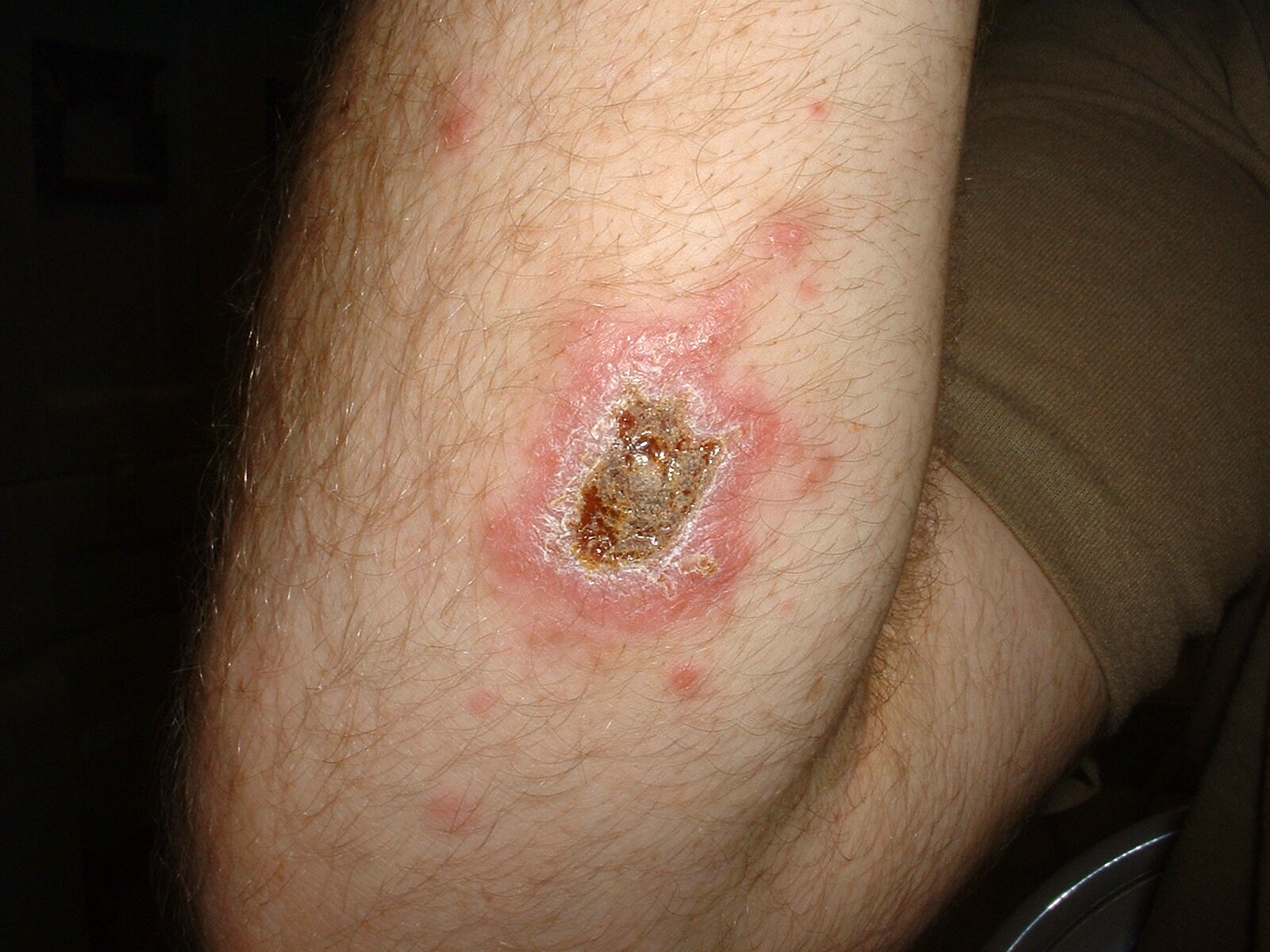
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is characterized by skin lesions limited only to areas vulnerable to bites: the face, the neck, the prearms, the lower parts of legs and the feet. This leishmaniasis is divided into Old World leishmaniasis (oriental) and a New World one. The incubation period lasts from several days to 6 months. Primary changes can be noticed around the bite spots. The lesions are about 2 – 10 mm wide. Then nodules appear that subsequently undergo necrosis and then ulceration. Inflammatory states appear near the ulceration. It heals after 2 -12 months but it leaves scars. Secondary bacterial infections also occur.
In disseminated leishmaniasis the first lesions are nodules, which spread. After closing the old nodules, new disseminated lesions appear on the face and limbs. This lesions might remain for years.
Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis occurs mostly in Brazil. In the infected mosquito bite spot a nidus appears, similar to that in cutaneous leishmaniasis. Promastigotes, transmitted by the insect spit form into a human body, they move into monocites and macrophages of the subcutaneous tissue and transform into another shapes. Secondary niduses develope in the mucosa areas. Skin lesions cover the mucosas of the anus, the vagina (women), the forskin (men). The incubation period lasts from 10 to 25 days, sometimes even a year!
The basic precautions that can be taken to prevent this disease are killing mosquitos, detecting and eliminating infection sources and curing infected people.