Taxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii)
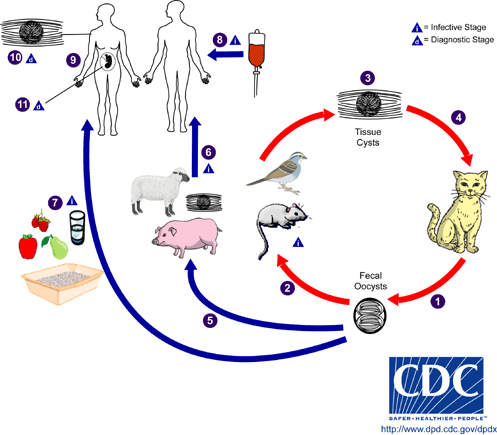
 Taxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii). Infectious disease of men and animals which is a result of protozoon – endocell organisms - infestation into different human organs. Under the supervision of an outline writing service, you will be able to better cover the topic and submit it in accordance with all requirements and norms. Toxoplasmosis is caused by toxoplasma gondii and belongs to cholimastix class of the protozoon kind. Cats are typical hosts. In their intestinal epithelial cells the whole life cycle takes place consisting of sexual and asexual phases. Two forms of the disease can be distinguished: acquired and inborn. Acquired toxoplasmosis does not have one clear clinical shape. It takes place when an infected female cat passes germs onto its foetus. It might cause miscarriage or pathological changes in characteristic locations that become visible in the offspring during the first years of life.
Taxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii). Infectious disease of men and animals which is a result of protozoon – endocell organisms - infestation into different human organs. Under the supervision of an outline writing service, you will be able to better cover the topic and submit it in accordance with all requirements and norms. Toxoplasmosis is caused by toxoplasma gondii and belongs to cholimastix class of the protozoon kind. Cats are typical hosts. In their intestinal epithelial cells the whole life cycle takes place consisting of sexual and asexual phases. Two forms of the disease can be distinguished: acquired and inborn. Acquired toxoplasmosis does not have one clear clinical shape. It takes place when an infected female cat passes germs onto its foetus. It might cause miscarriage or pathological changes in characteristic locations that become visible in the offspring during the first years of life.
Acquired toxoplasmosis symptoms:
- swollen absorbent glands mostly in the neck
- intense headache
- uncharacteristic fever – usually not high
- meningitis
- spleen enlargement
- miscarriage, delivery of a dead foetus or alive with toxoplasmosis symptoms
- inflammation of the uterus membrane
- enlarged liver
- transient rashes
- conjunctivitis
- throat inflammation
Chronic toxoplasmosis symptoms:
- fever
- limbs and joints pain
- chronic headaches
- mental disorders
- organic symptoms of the absorbent glands, the liver, the spleen, the eyes, the central nervous system and the uterus (endometritis)
- miscarriage, delivery of a dead foetus or alive with toxoplasmosis symptoms
Inborn toxoplasmosis symptoms:
- hydrocephalus
- intracerebral calcification
- conjunctivitis and choroiditis
- jaundice
- enlargement of the liver and spleen
Infection sources:
- directly from an infected cat (only cat, never from other animals)
- through the alimentary canal (contaminated food, vegetables, fruit)
- by eating fresh, grilled or smoked meat
- through damaged skin (vets, laboratory workers) or anus mucosa (homosexualists)
Disease course
The parasite moves from the alimentary canal of a human into the absorbent glands, the muscles, the brain, the spinal cord and the eye balls. The course of the disease can be quite asymptomatic. However often the following symptoms may occur: enlarged absorbent glands, constipation, rarely – heart muscle inflammation or meningitis. The infection of women before they get pregnant does not carry any risk for the future foetus (however there are still some specialist who do not agree with this thesis). Fresh infection of a pregnant woman causes an inflammation of the placenta and this way the parasites may penetrate into the foetus. The risk of toxoplasmosis penetration through the placenta increases along with the pregnancy progress: 25% – in the first trimester, 50% – in the second one and 65% – in third one. Whereas in the inborn form of toxoplasmosis the risk is the highest in the first trimester and equals 75%, in the second one – 50% and the third one – 5%.
Inborn toxoplasmosis might cause foetal hypertrophy, thrombocytopenia, enlarged liver and spleen. Natural miscarriage or intrauterine death occur in the first trimester of the pregnancy. Symptomatic inborn toxoplasmosis occurs in 30% of infected infants, 10% of which suffer from its acute course.
Perinatal death rate caused by inborn toxoplasmosis is estimated at 8%. 70% of prenatally infected children do not show any symptoms and in most of them the disease is left undetected and not cured. In some children at later age certain consequences connected with the central nervous system, hearing handicap and vision disorders might appear.
Who is the most vulnerable to toxoplasmosis infection ?
Toxoplasmosis infection risk increases with age. Research has shown that mothers who gave birth to a child with Down syndrome had the positive result of an analysis on toxoplasmosis in 80% of cases; women with pathologica obstetric anamnesis – 60%; the mentally ill – 40 – 50% and people with eye sickness – 50 – 60 %.