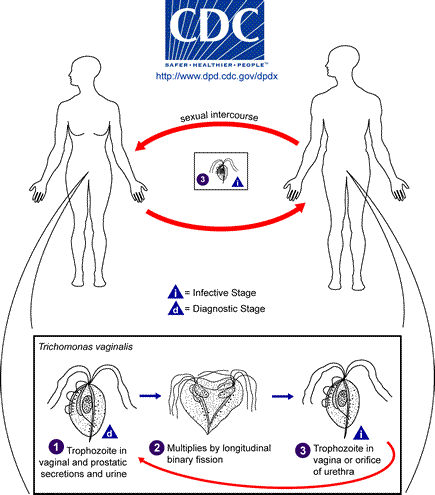
Trichomonas vaginalis
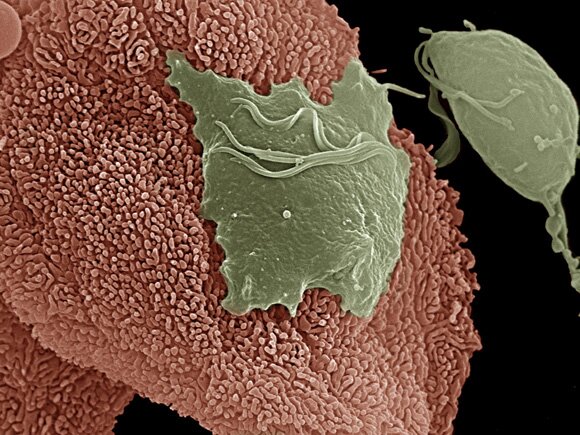
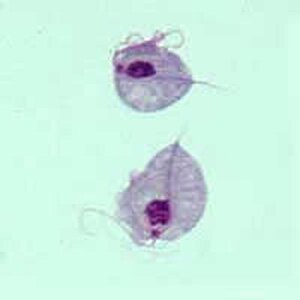 Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomonas vaginalis is quite common in Europe and it belongs to chilomastix family which is mainly sexually transmitted. In chronic inflammatory states, in case of women, it can be found in the vagina or urethra and when it comes to men it occurs in the urethra and prostate and seminal gland.
Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomonas vaginalis is quite common in Europe and it belongs to chilomastix family which is mainly sexually transmitted. In chronic inflammatory states, in case of women, it can be found in the vagina or urethra and when it comes to men it occurs in the urethra and prostate and seminal gland.
Pregnant women can transmit the disease to their babies while giving birth (it usually disappears after a month). Trophozoites of the size of 7×10 cm cause vagina epithelium cells damages, small losses and ulceration. The hatching period lasts 1 – 4 weeks. 50% of infected women suffer from ample foaming yellow vagina discharge and it is accompanied by vagina and vulva irritation. The symptoms intensify during menstruation. Medical examination can proove an iflammation of the vagina, an increased amount of mucus in the vagina or its damage.Trichomoniasis is often complicated by bacterial and fungal infection. Trichomoniasis treatment intensifies candidosis activity as a result of changes in vaginal biocenosis. Chronic trichomoniasis might influence pelvis minor inflammatory states, infertility, pregnancy complications, the length of convalescence period after hysterectomy. In case of men the trichomonas might embed in the urethra, prostate gland, testicles and penis ulceration.The invasions generally show no symptoms and it must be distinguished from infection and diploccocus gonorrhoea.
Trichomoniasiasis complications
It is usually accompanied by bacterial and fungus infection (e.g. Candidia albicans). If it is chronic and not cured it can cause infertility and serious pregnancy complications.
Trichomonas vaginalis symptoms:
- ample foaming stinking mostly yellow or greenish discharges
- itching, burning
- pain in the perineum area
- vagina and vulva irritation
When an infection of the reproductive ducts is accompanied by a urethra ducts infection there is a possibility of itchiness, over-urination or painful urination and pain in the lower part of the stomach.